Exercise \- Debug SBL on QEMU with GDB
This page is to provide basic GDB usage on QEMU target for better understanding SBL flow.
Prepare SBL QEMU image
By default, SBL uses compile optimization for binary size and code speed. The compile optimization sometime makes source level debugging hard to use.
$ cd /path/to/slimbootloader/ $ python BuildLoader.py build qemu
Launch QEMU target
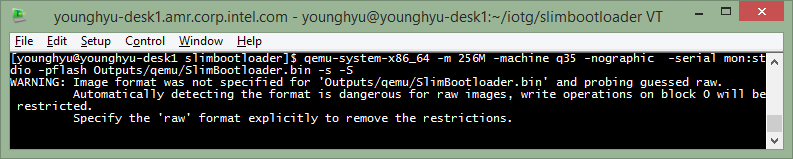
Open a terminal to launch the target and launch the target with ‘-s -S’ option.
$ cd /path/to/slimbootloader/
$ qemu-system-x86_64 -m 256M -machine q35 -nographic -serial mon:stdio -pflash Outputs/qemu/SlimBootloader.bin -s -S
Launch GDB
Open an another terminal and launch GDB with helper script and ‘-tui’(Text UI) option:
$ cd /path/to/slimbootloader/
$ cd Platform/QemuBoardPkg/Script
$ gdb -x gdbinit -tui
There are useful tui commands.
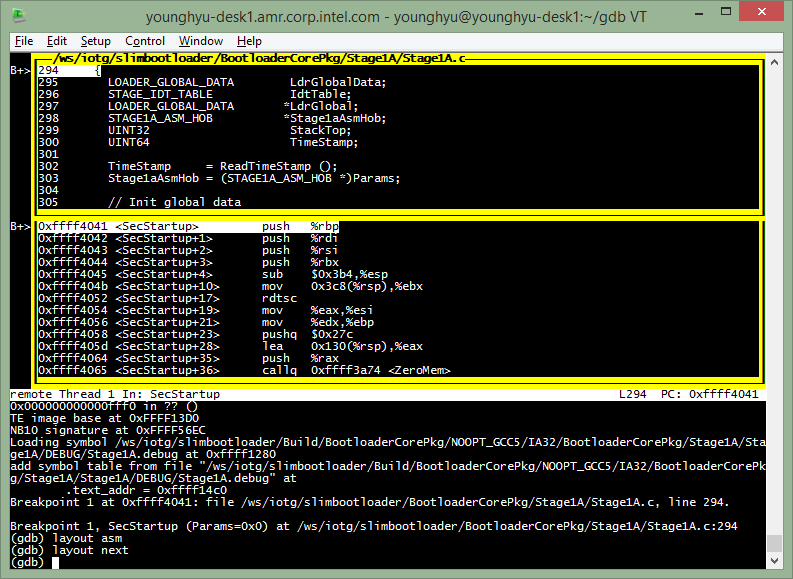
(gdb) layout asm
(gdb) layout src
(gdb) layout reg
(gdb) layout next
(gdb) focus src
(gdb) focus asm
(gdb) focus cmd
Here are basic gdb commands.
(gdb) quit (=q, quit gdb session)
(gdb) continue (=c, continue to execute code)
(gdb) step (step program until it reaches a different source line)
(gdb) stepi (step one instruction exactly)
(gdb) next (step program, proceeding through subroutine calls)
(gdb) nexti (step one instruction, but proceed through subroutine calls)
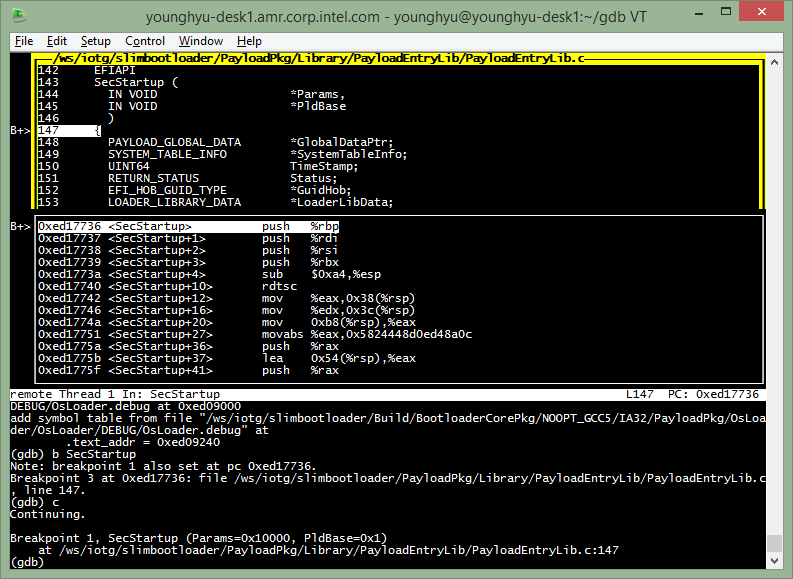
(gdb) break SecStartup2 (=b SecStartup2, break at SecStartup2)
(gdb) break *0xffff4052 (=b *0xffff4052, break at 0xffff4052 memory)
(gdb) print LdrGlobalData (p LdrGlobalData, print value of LdrGlobalData)
(gdb) print/x LdrGlobalData->Signature (p/x LdrGlobalData->Signature, print value of LdrGlobalData->Signature in hex value)
(gdb) info registers (=i r, print general registers)
(gdb) info all-registers (=i al, print all registers)
(gdb) info breakpoints (=i b, print all break points)
(gdb) info locals (=i lo, print local variables)
(gdb) info variables (=i va, print all global and local variables)
(gdb) info stack (=i s, print call stack)
(gdb) list SecStartup2 (=l SecStartup2, show SecStartup2 code in TUI source window)
(gdb) list 346 (=l 346, show line#346 in TUI source window)
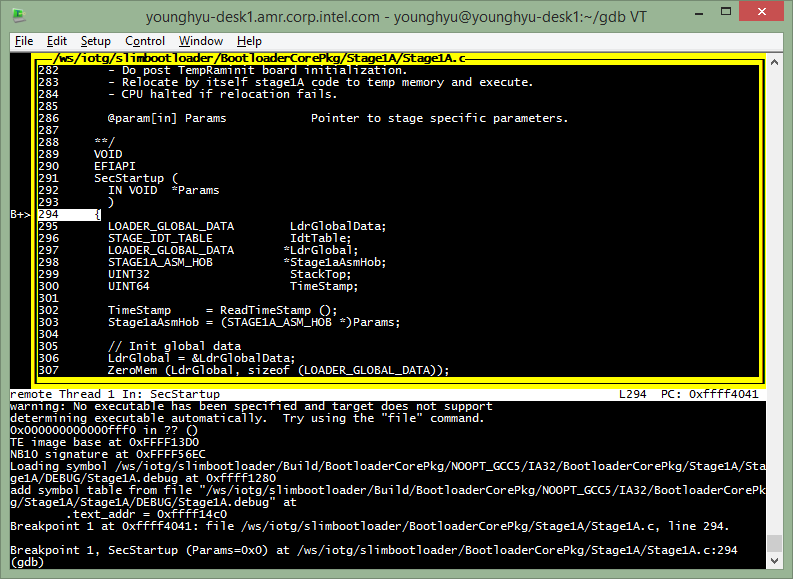
Transit Stage1A to Stage1B
Let’s set a breakpoint before relative execution of ContinueFunc(). See, ContinueEntry (&Stage1aHob) in Stage1A.c.
(gdb) l 272 (to see the code around ContinueEntry (&Stage1aHob);, line# may change)
(gdb) b 272 (set a breakpoint at ContinueEntry (&Stage1aHob);)
(gdb) c (continue to next breakpoint)
(gdb) b *0xfffff3b3 (set a breakpint at callq *%rdx, address may change)
(gdb) c
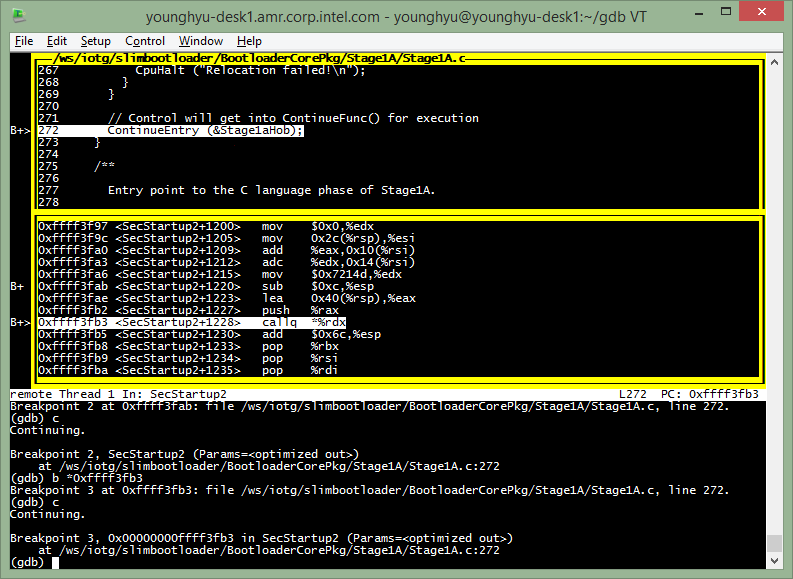
Do step one instruction exactly with stepi(=si) command for relative code execution.
(gdb) si
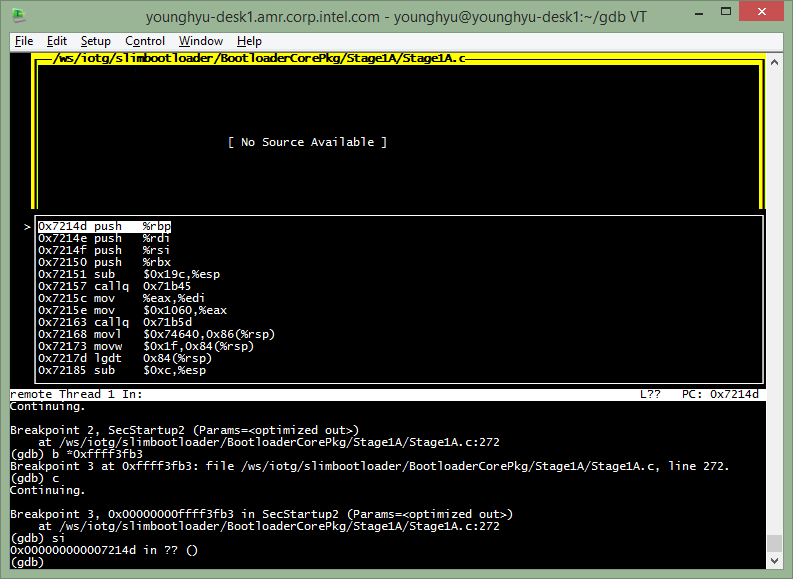
No source avilable in source window because ContinueFunc is relative executed, so no symbol match found. Now, it’s time to run loadthis again to re-load proper symbol.
(gdb) loadthis
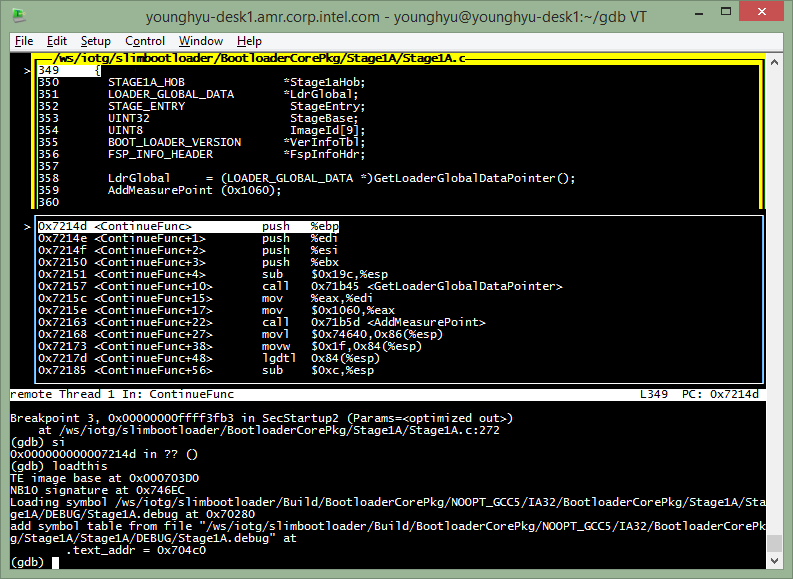
Now, we are at the beginning of Stage1A ContinueFunc(). The transition to Stage1B is done in StageEntry() at the end of ContinueFunc(). Let’s set a breakpoint before going to Stage1B entry point.
(gdb) l 407 (to see around StageEntry() code, line# may change)
(gdb) b 407 (set a breakpoint at StageEntry(), line# may change)
(gdb) c
(gdb) b *0x72a14 (set a breakpoint at call *%eax, address may change)
(gdb) c
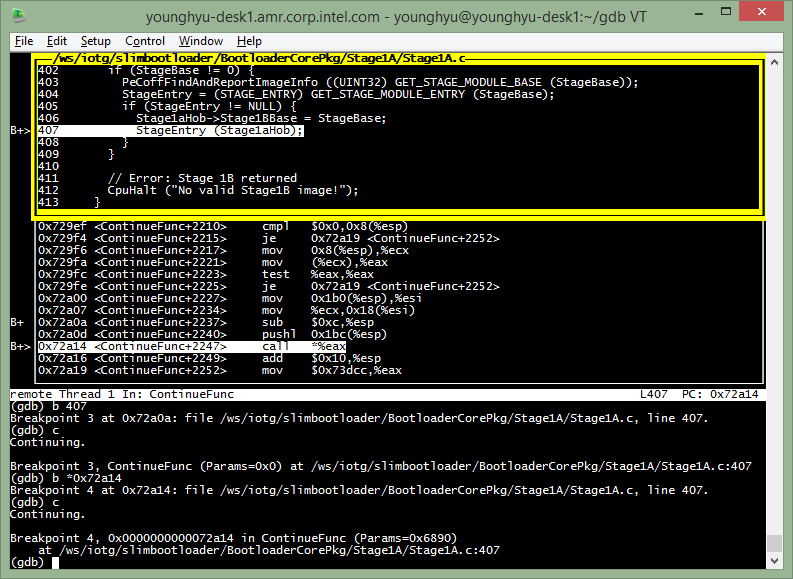
Let’s go into Stage1B with stepi(=si) command, re-load symbol and get to Stage1B SecStartup.
(gdb) si (no source available again, time to re-load symbol)
(gdb) loadthis
(gdb) b SecStartup
(gdb) c
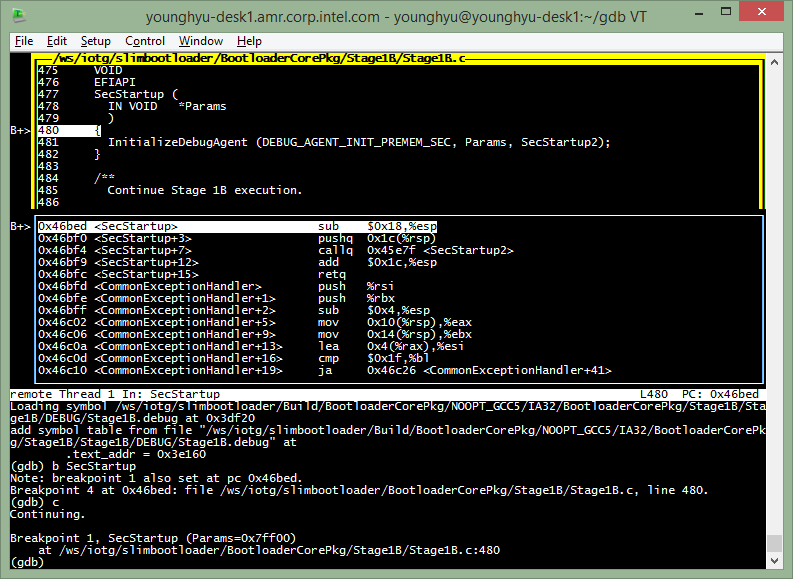
Transit Stage1B to Stage2
Now we are at SecStartup in Stage1B. The transition from Stage1B to Stage2 is done at the end of Stage1B ContinueFunc().
Let’s break before SwitchStack() at the end of ContinueFunc().
(gdb) l 567 (to see the end of ContinueFunc(), line# may change)
(gdb) b 567 (set a breakpoint at SwitchStack(), line# may change)
(gdb) c
(gdb) p/x ((STAGE_HDR *)Stage2Hob->Stage2ExeBase)->Entry
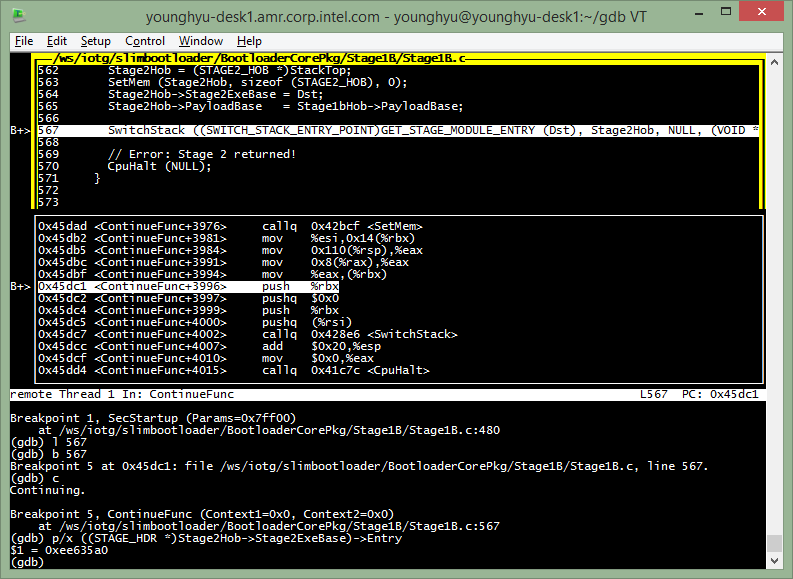
The returned address ‘$n = 0xee635a0’ is Stage2 entry point. Let’s set a breakpoint at the address and stop at Stage2 SecStartup.
(gdb) b *0xee635a0
(gdb) c
(gdb) loadthis (to re-load Stage2 symbol)
(gdb) b SecStartup
(gdb) c
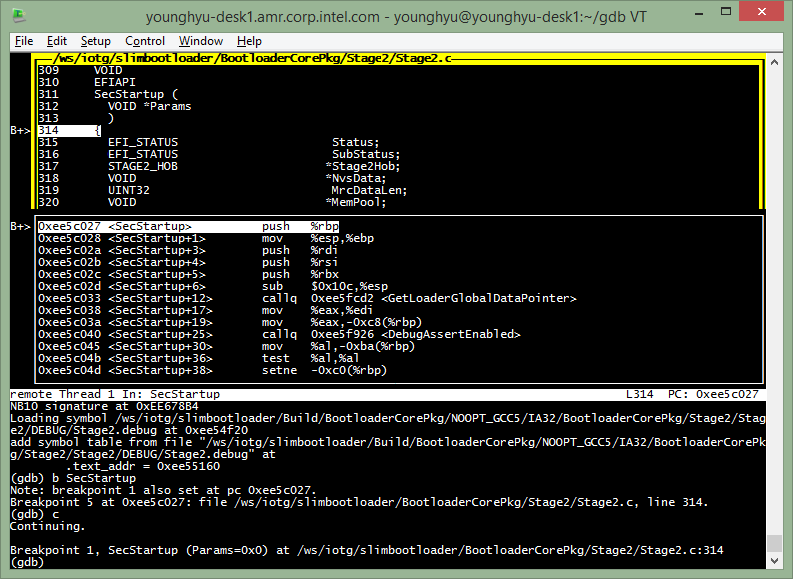
Transit Stage2 to Payload
Now we are at SecStartup in Stage2. The transition from Stage2 to Payload is done at the end of Stage2 NormalBootPath().
Let’s break before PldEntry() at the end of NormalBootPath().
(gdb) l 252 (to see the end of NormalBootPath(). line# may change)
(gdb) b 252 (set a breakpoint at PldEntry (PldHobList, (VOID *)PldBase))
(gdb) c
(gdb) b *0xee5e428 (set a breakpoint at callq *-0xb8(%rbp) before calling PldEntry)
(gdb) c
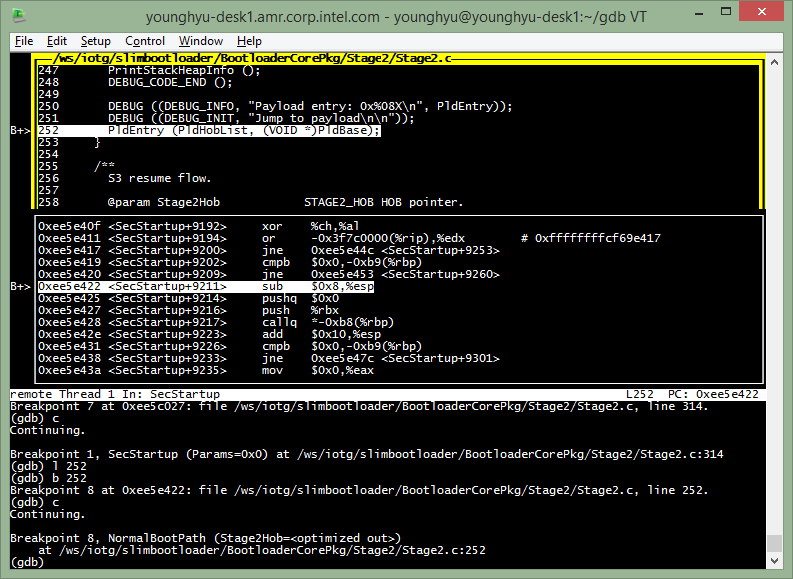
Let’s go into Payload with stepi(=si) command, re-load symbol and get to Payload SecStartup.
(gdb) si
(gdb) loadthis
(gdb) b SecStartup
(gdb) c